Gateware TCL Scripts Structure#
This document describes the structure of the gateware TCL scripts. It is of interest to understand how to extend or customize the gateware.
The Libero SoC TCL Command Reference Guide describes the TCL command used in the gateware scripts.
Gateware Project#
The gateware project is made up of:
TCL scripts
HDL/Verilog source code
IO pin constraints
Placement constraints
Device tree overlays
All these files are found in the FPGA-design directory.
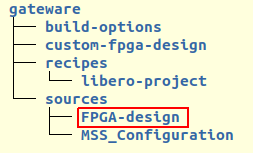
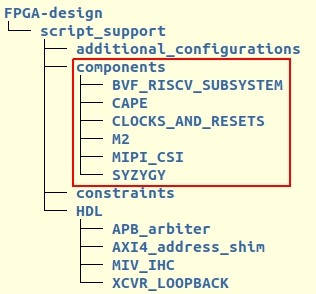
Gateware Components#
The gateware is organized into 6 components:
Clocks and reset control
A base RISC-V microprocessor subsystem
Cape interface
M.2 interface
MIPI camera interface
SYZYGY high speed interface
Gateware Build Options#
Each interface component may have a number of build options. For example, which cape will be supported by the generated gateware.
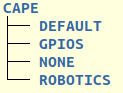
The name of the directories within the component’s directory are the option names passed to the top Libero BUILD_BVF_GATEWATE.tcl script. These directory names are the option name specified in the bitstream builder’s build option YAML files.
The gateware is extended or customized by creating additional directories within the component directory of interest. For example, add a MY_CUSTOM_CAPE directory under the CAPE directory to add a gateware build option to support a custom cape.
Gateware Component Directories#
The component directory contains subdirectories for:
Constraint files
Device tree overlay
Optional HDL/Verilog source code

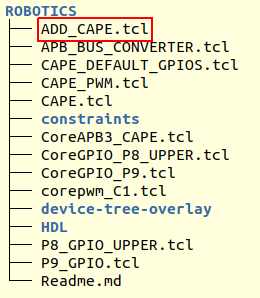
Gateware TCL Scripts#
The component directory contains the TCL scripts executed by Libero to generate the gateware. The TCL script framework executes a hand-crafted ADD_<COMPONENT_NAME>.tcl script which instantiates the component and stiches it to the base RISC-V subsystem and top level IOs. The other TCL scripts are typically IP configuration scripts and SmartDesign stiching scripts.
Opening the gateware as a libero project#
It can be slightly difficult to explore the gateware design through the TCL files. To inspect the gateware design in detail easily, you can open the gateware as a Libero project. This is done by running the following command in the gateware directory:
python build-bitstream.py ./build-options/default.yaml # build option depending on the gateware
You will need to have all microchip tools installed and the environment variables set up correctly. Refer to the `microchip tools installation guide<mchp-fpga-tools-installation-guide>`_ for information on how to install these tools.
